Table of Contents

Weed cultivation is gaining popularity for its appeal to self-sufficiency, organic farming, and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced horticulturist, this guide unveils the secrets to growing robust cannabis plants, achieving bountiful harvests, and producing high-quality buds. Even if you’re new to growing, this guide will help you become a successful cultivator, potentially yielding up to 10 ounces of premium bud per plant in just three months.
4 Steps to begin Cannabis Plant
Step 1: Check Local Laws
Before delving into the realm of cannabis cultivation, it’s imperative to ascertain its legality within your jurisdiction. Every state within the United States possesses its own set of regulations governing the cultivation of homegrown cannabis. Divergent approaches are observed, with certain states treating recreational and medicinal cultivation on an equal footing, while others delineate distinct guidelines for medical cannabis patients and recreational enthusiasts. Furthermore, specific states exclusively authorize the cultivation of medical cannabis by individual residents.
In the United States, the states currently have three types of laws regarding marijuana cultivation: fully legal, partially legal, and fully illegal. Next, we will use three tables to explain the marijuana legislation in each state (data as of February 2024).
The states where marijuana cultivation is fully illegal include:
Alabama, Florida, Idaho, Indiana, Kansas, Kentucky, Nebraska, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, South Carolina, Tennessee, Texas, Wisconsin, and Wyoming.
The states where marijuana cultivation is partially illegal include:
The states where marijuana cultivation is fully illegal include:
Step 2: Creating Ideal Environment
In this step, we explore the key considerations when deciding between indoor and outdoor cannabis cultivation. We discuss the advantages and disadvantages of each, including aspects like climate control, privacy and security, pest management, consistency of results, costs, quality control, and the learning experience. This step helps you make an informed choice tailored to your preferences and goals for successful cannabis cultivations.
Pros and Cons of Indoor vs. Outdoor Cannabis Cultivation
Benefits of Growing at Home
Save money by growing your own fruits, vegetables, herbs, and flowers instead of buying them
Access to fresh, organic produce since you control growing conditions and inputs
Ability to grow heirloom, exotic, or hard to find varieties not found in stores
Know exactly how your plants are grown from seed to harvest
Convenience of having ingredients and garnishes right at your fingertips
Better tasting produce that’s harvested at peak ripeness
Satisfaction of nurturing plants through their entire life cycle
Creative outlet and stress relief from tending a garden
Step 3: Selecting Right Cannabis Strain
When choosing the perfect cannabis strains for your cultivation, it is crucial to consider various factors that suit your preferences and goals. Here are some factors you might need to consider :
1. Indica vs Sativa
Indica strains often provide relaxing effects, while sativa strains tend to be more energizing. Select the one that aligns with your desired experience. Additionally, you can explore hybrid strains that combine characteristics of both.
2. Growth Duration
Some strains have a shorter growth period, ideal if you’re looking for quicker results. Longer growth duration strains might be more challenging but offer unique qualities.
3. Plant Size
Assess your available space. If you have limited room, choose smaller, compact strains, while larger areas can accommodate taller, bushier plants.
4. THC and CBD Content
Decide on the balance of THC (psychoactive) and CBD (non-psychoactive) that suits your needs. High THC strains are more potent, while higher CBD strains are more therapeutic.
5. Personal Preferences
Ultimately, the strain you choose should align with your personal taste and medicinal requirements. It takes 24 to 72 hours, with an ideal temperature range of 70-85℉ and 70% humidity. Use the paper towel method for germination or soak seeds in water. A taproot indicates successful germination within 2 to 4 days.
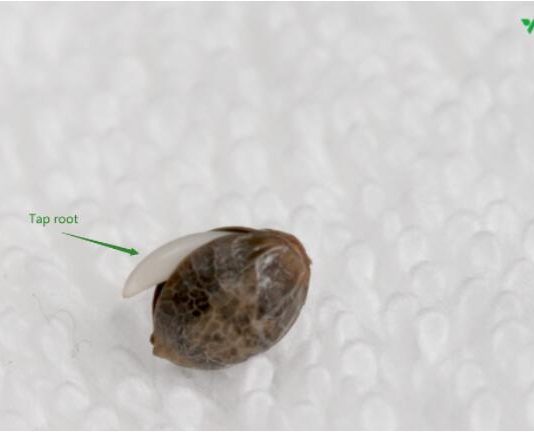

Step 4 : Seed Germination
Germination is crucial, turning a dormant seed into a vibrant seedling. It takes 24 to 72 hours, with an ideal temperature range of 70-85°F and 70% humidity. Use the paper towel method for germination or soak seeds in water. A taproot indicates successful germination within 2 to 4 days.
6 Tips for Successful Germination
- Start with high-quality, fresh seeds with high germination rates
- Use the paper towel method – Place seeds between moist paper towels in a warm, dark space until they sprout
- Maintain moisture, but do not oversaturate. Mist paper towles as needed
- Use a seedling heat mat which provides consistent, ideal warm temperatures to speed up germination
- Patience, patience and still patience. Resist Peeking ! Germination takes time
- Find your ideal grow box, enabling you to optimize the cultivation of your weed with remarkable efficiency
FAQs about how to grow weed
How long does it take to grow weed from seed to harvest ?
The entire process usually takes 3-5 months, depending on the strain, growing conditions, and whether you’re growing indoors or outdoors.
Is it easy to grow weed at home ?
Cannabis can be relatively easy to grow at home, especially with the right knowledge and preparation. Starting with beginner-friendly strains, following proper care techniques, and addressing any issues promptly can lead to successful cultivation.
What is the best method of growing weed ?
The best method of growing weed depends on your circumstances and preferences. Common methods include indoor soil cultivation, hydroponics, and outdoor growing. Indoor cultivation offers more control over environmental factors, while outdoor growing utilizes natural sunlight. The best method for you depends on your resources and experience.
How much weed can I get off 1 plant ?
The yield from one cannabis plant can vary widely based on factors like strain, growing conditions, and expertise. On average, a single plant can yield anywhere from a few ounces to a few dozen ounces. High-yielding strains and optimal growing conditions tend to produce more substantial harvests.
Is growing weed easy to grow ?
Growing weed can be relatively easy or moderately challenging, depending on your approach and experience. Beginner-friendly options, such as the all-in-one smart grow box – VGrow, can make the process straightforward, even for those with minimal gardening experience.
How hard is it to start growing weed ?
Starting to grow weed can be as easy or as challenging as you choose to make it. Beginners are encouraged to begin with simple, user-friendly methods, such as using the all-in-one smart grow box – VGrow, designed for ease of use and accessibility. Basic techniques like soil-based cultivation and beginner-friendly strains can provide a relatively easy entry point. As you gain experience, you can explore more advanced techniques and strains with specific requirements.
What is needed to grow good weed ?
To grow high-quality cannabis, you’ll need the following:
Good Genetics: Start with high-quality seeds or clones from reputable sources. The quality of your starting material will significantly impact the final product. For an easier and accessible approach, consider all-in-one smart grow box – VGrow, which simplifies the process of starting your cultivation journey.
Proper Environment: Maintain the right temperature, humidity, and airflow in your growing space. VGrow’s smart ecosystem, coupled with its built-in environmental controls, creates the perfect nurturing environment for your plants.
Quality Lighting: Invest in good grow lights, such as LEDs, HIDs, or fluorescent lamps, to provide the necessary spectrum and intensity for your plants. VGrow features advanced Samsung LM301H EVO LED lights designed to optimize plant growth automatically.
Nutrients: Use a suitable nutrient regimen and understand the nutrient needs of your plants at different growth stages. VGrow’s intelligent app, GrowPilot, provides you with growth algorithms and notifications for proper plant nutrition.
pH Control: Monitor and adjust the pH of your water or growing medium as needed to ensure optimal nutrient uptake.
Watering and Irrigation: Provide your plants with consistent and well-managed watering to prevent overwatering or underwatering. VGrow offers various irrigation options to help with this.
Space: Ensure you have enough space for your plants to grow. Consider VGrow’s compact design for easy integration into your indoor space.
Patience: Growing high-quality weed takes time. Cannabis goes through several growth stages before it’s ready for harvest. With VGrow, you can simplify the process and make it more accessible even for those with minimal growing experience.
Conclusion
Remember that growing weed can be a rewarding hobby, and your success will improve with experience. It is important to continue learning and refining your tec hniques to achieve better results.
Vivosun also provides other articles on cannabis cultivation. If you share similar questions, feel free to refer to blogs as follows:
There are several benefits to growing at home: Benefits of Growing at Home Introducing VGrow – The All-In-One Automated Smart Grow Box VGrow, the all-in-one self-sustaining grow box , tackles all the indoor growing challenges you’ve faced before. We love the Vivosun Smart Grow System and we’re certain that you too will love it once you try it