When it comes to growing marijuana, enthusiasts have two primary methods: hydroponic and soil cultivation. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, catering to different preferences and requirements of growers. In this article, I will share with you my experience with using different cultivation methods, specifically hydroponic weed and soil weed, examining their pros and cons to help you decide which method suits you best.
Table of Contents
What is Hydroponic Weed?
Hydroponic weed refers to marijuana that is cultivated without the use of soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution, allowing them to absorb essential nutrients directly through their roots. This method relies on various hydroponic systems such as deep water culture, nutrient film technique, and aeroponics.
Hydroponic Growing: Pros and Cons
Pros:
1. Enhanced Water Efficiency: Hydroponic cultivation conserves water significantly compared to soil-based farming, using up to ten times less water.
2. Increased Crop Yields: Controlled environments and optimized nutrient delivery in hydroponics can lead to higher crop yields with faster growth rates.
3. Utilization of Minimal Space: Hydroponic setups can be established in compact spaces, ideal for urban areas and regions with limited agricultural land.
4. Pesticide-Free Environment: Reduced risk of soil-borne pests and diseases in hydroponic systems means less need for pesticides.
5. Protected Growing Conditions: Enclosed environments shield plants from harsh weather, pests, and diseases, ensuring more consistent crop production.
6. Precise Nutrient Control: Growers have precise control over nutrient composition and pH levels, optimizing plant growth.
7. Accelerated Growth Rates: Direct access to nutrients and water in hydroponic systems accelerates plant growth, leading to quicker harvests.
Cons:
1. Costly Infrastructure Investment: High initial setup costs may deter new growers due to specialized equipment and technology requirements.
2. Dependence on Stable Power Supply: Hydroponic systems require consistent electricity supply for operation, posing risks during power outages.
3. Demand for Diligent Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuous monitoring and upkeep are essential for maintaining optimal growing conditions, requiring significant attention.
4. Need for Knowledge and Expertise: Successful hydroponic farming necessitates understanding nutrient management, pH regulation, and system maintenance.
5. Limitations on Crop Variety: Not all plants thrive in hydroponic environments, limiting the range of cultivable crops.
Hydroponic cultivation offers numerous benefits, including higher yields and efficient space usage, but it requires careful management and significant initial investment. Ultimately, the choice between hydroponics and traditional farming depends on specific needs and resources available.
What is Soil Weed?
Soil weed, on the other hand, refers to marijuana that is grown in traditional soil-based environments. This method utilizes natural soil or soil mixes enriched with organic nutrients to support plant growth.
Soil-Based Growing: Pros and Cons
Pros:
1. Natural Nutrient Supply: Soil inherently contains diverse nutrients and organic matter essential for plant growth, reducing the need for additional fertilizers.
2. Microbial Support: Soil hosts a diverse microbiome aiding in plant health and nutrient absorption, fostering better growth.
3. Ease of Setup: Soil-based methods are simpler to establish and require less technical expertise, making them accessible for beginners.
4. Cost-Effectiveness: Initial costs for soil-based cultivation are typically lower, with basic materials like pots and soil being affordable and widely available.
5. Versatility: Suitable for both indoor and outdoor settings, soil-based cultivation offers flexibility across various environments.
Cons:
1. Pest and Disease Vulnerability: Soil can harbor pests, diseases, and weeds, necessitating pesticide and herbicide use to mitigate risks.
2. Variable Soil Quality: Soil quality varies widely, with issues like pH imbalances, compaction, and poor drainage hindering plant growth in some cases.
3. Resource Intensity: Soil-based agriculture demands significant water, land, and fertilizer inputs, potentially leading to soil degradation and erosion over time.
4. Slower Growth and Lower Yields: Plants grown in soil often exhibit slower growth and lower yields compared to hydroponic systems, as they expend energy seeking nutrients in the soil.
5. Environmental Impact: Conventional soil-based farming practices can contribute to environmental issues such as high water usage, fertilizer runoff, and biodiversity loss.
In conclusion, soil-based cultivation offers natural nutrient provision, microbial support, ease of setup, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. However, challenges including pest vulnerability, variable soil quality, resource intensity, slower growth, and environmental impact must be considered. The choice between soil-based and soilless (hydroponic) cultivation depends on growers’ priorities, resources, and crop needs.
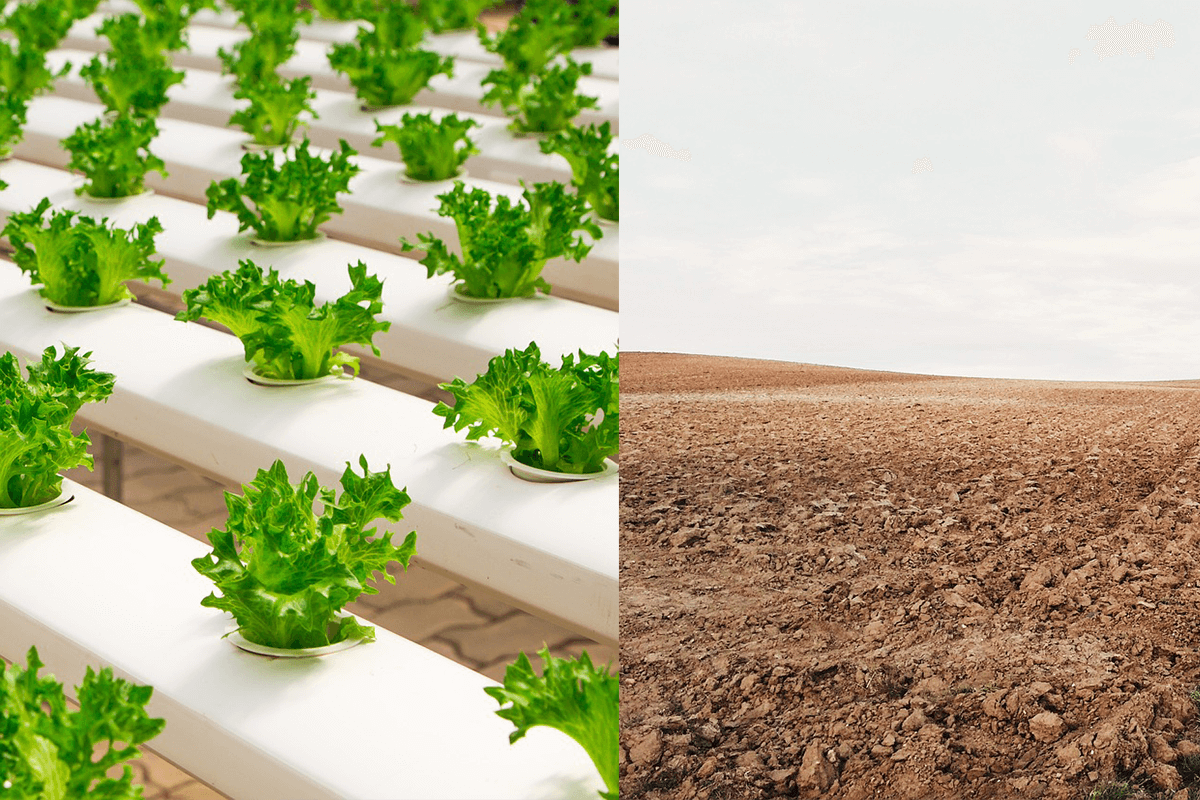

Hydroponic Weed vs. Soil Weed: A Comparison
Growth Process Comparison
Hydroponic weed typically exhibits faster growth rates due to direct nutrient uptake, whereas soil weed may take longer to reach maturity.
Yield Comparison
While hydroponic systems can yield higher quantities of marijuana per square foot, soil cultivation often produces plants with larger yields per individual plant.
Nutrient Control Comparison
Hydroponic setups allow precise control over nutrient levels, ensuring optimal plant health. In contrast, soil cultivation relies on natural decomposition processes to release nutrients, leading to less precise control.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Hydroponic cultivation requires less water and space compared to soil cultivation, making it a more environmentally friendly option. However, the energy consumption associated with indoor hydroponic setups may offset these benefits.
How to Grow Hydroponic Weed
Ready to take the plunge into hydroponic cultivation? Here’s what you’ll need to get started.
Equipment Needed
Step-by-Step Process
- Set up your hydroponic system according to the instructions.
- Keep an eye on your pH levels – you want them to be just right for your plants.
- Pop your seeds or clones into the system and watch ’em grow!
- Make sure your plants get plenty of light and fresh air.
- Check your nutrient levels regularly and adjust as needed.
- Harvest your buds when they’re nice and ripe – it’s like picking fruit from a magical garden!

FAQs
Which method produces higher-quality weed?
Both hydroponic and soil cultivation can produce high-quality marijuana, but factors such as genetics, growing conditions, and post-harvest processes also play significant roles.
Is hydroponic weed safer to consume than soil weed?
The safety of marijuana depends on various factors, including cultivation practices, pesticide use, and testing procedures. Both hydroponic and soil weed can be safe if grown responsibly.
Can I switch from soil to hydroponic cultivation or vice versa?
Yes, it is possible to transition between cultivation methods, but it may require adjustments to growing techniques and equipment.
Which method is more cost-effective in the long run?
The cost-effectiveness of each method depends on factors such as initial investment, ongoing maintenance, and desired yield. Some growers may find hydroponic systems more cost-effective over time, while others prefer the simplicity of soil cultivation.
Are there any legal implications associated with hydroponic or soil cultivation?
Laws regarding marijuana cultivation vary by jurisdiction, so it’s essential to research and comply with local regulations regardless of the chosen cultivation method.
Is hydroponic better than soil for weed?
In many cases, hydroponic cultivation of cannabis offers several significant advantages over soil cultivation. Hydroponic systems provide precise nutrient control, allowing plants to more efficiently absorb essential nutrients. This method also reduces the risk of pests and diseases, as there are no soil-borne microbes or parasites. Additionally, hydroponics can accelerate plant growth and often result in higher yields. However, hydroponic systems require more technical expertise and management, with higher initial costs. Therefore, when choosing a cultivation method, it’s essential to weigh these pros and cons. The following images illustrate a comparison between hydroponic systems and soil cultivation.
Conclusion
Both hydroponic weed and soil weed offer unique benefits and drawbacks to growers. While hydroponic cultivation provides faster growth and greater nutrient control, soil cultivation offers simplicity and environmental sustainability. Ultimately, the choice between the two methods depends on individual preferences, resources, and goals.